The chemical industry is constantly seeking innovative technologies to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and maintain high product quality. Damo’s PV membrane separation solution has emerged as a groundbreaking solution for dehydration in various industries. In this blog post, we will discuss how Damo’s cutting-edge technology is transforming acetone dehydration in a Jiangsu-based company, demonstrating the potential of this advanced technique.
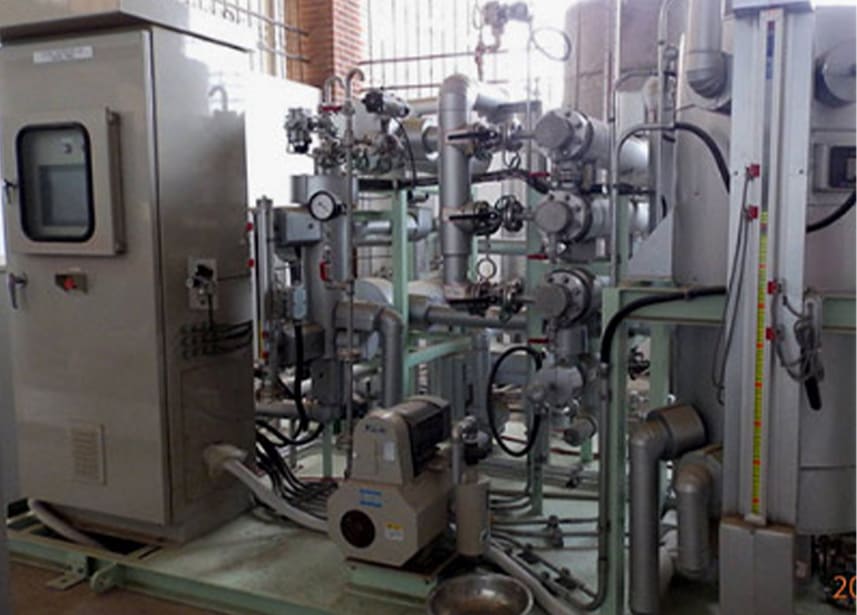

A Successful Case Study: Jiangsu Company’s Acetone Dehydration Project
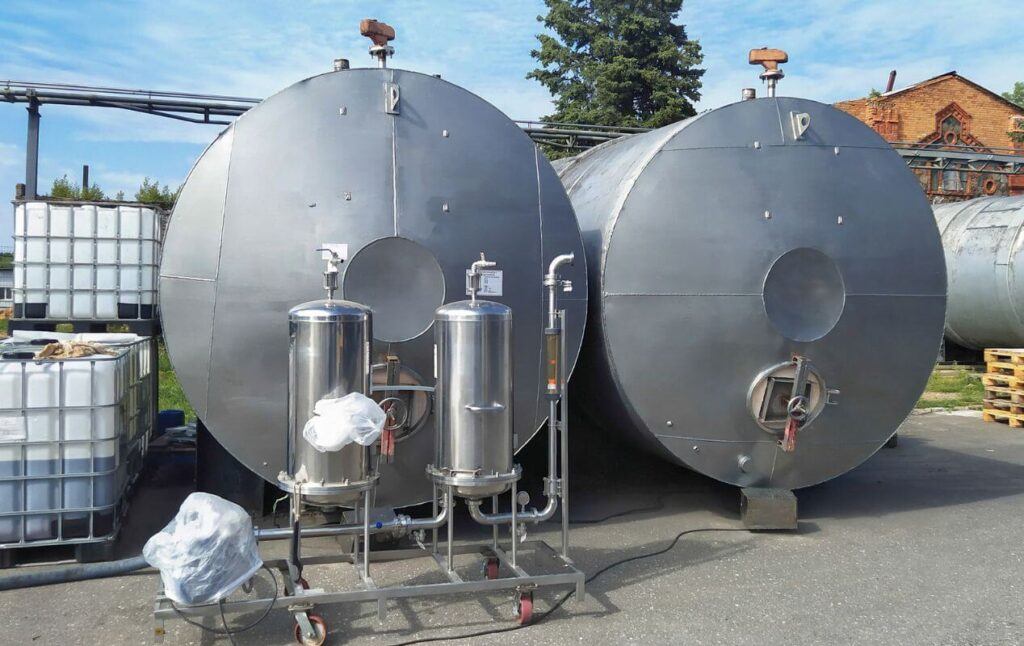
The Jiangsu company implemented Damo’s PV membrane separation solution for their acetone vapor-phase dehydration project, achieving an annual production capacity of 1,500 tons. The technology effectively reduced the water content in acetone from 6% to 0.2%, demonstrating the power of Damo’s membrane technology.
Collaborative Innovation: Damo’s Partnerships with Leading Research Institutions
Damo has established close cooperation with top-tier research institutions such as the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian University of Technology, and Tianjin University. These collaborations have brought together leading experts, including professors and researchers, to develop advanced membrane separation, distillation, and adsorption integration technologies. As a result, Damo has emerged as a leader in the field of acid-resistant (pH<5) pervaporation dehydration membranes.
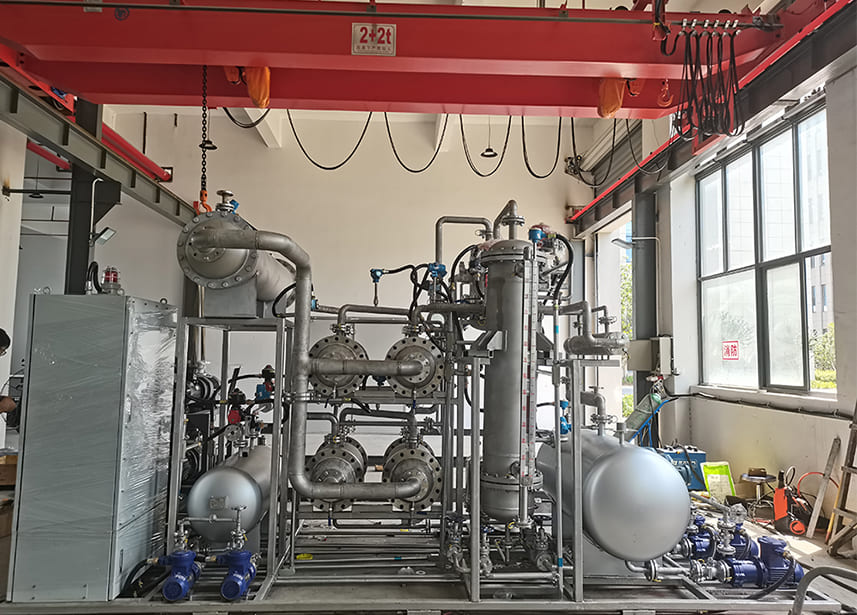
Highly Integrated Technology: Combining Adsorption, Membrane Separation, and Distillation
Damo’s technology combines adsorption, membrane separation, and distillation processes to treat complex organic solvent systems and recover valuable materials. The company has conducted a series of experiments on various solvent systems, obtaining crucial process data and developing comprehensive integrated technology solutions, process control systems, and complete equipment sets.
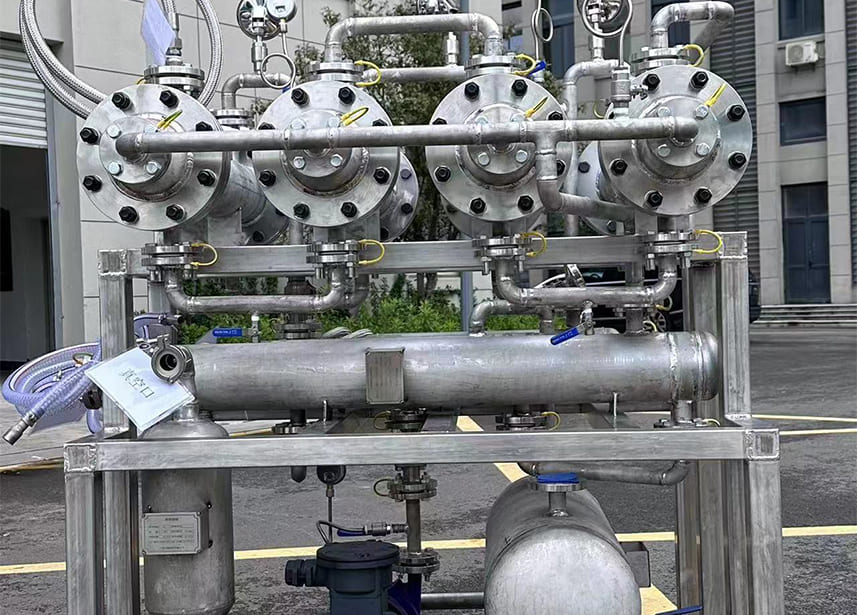
Pervaporation Membrane Dehydration Technology: Key Components
The dehydration technology consists of several key components, including evaporators, heat exchangers, membrane modules, condensers, vacuum systems, and PLC systems. During the dehydration process, the feed material is heated and enters the feed side of the membrane module. Meanwhile, the permeate side is maintained under a low-pressure environment through a vacuum. Water molecules preferentially permeate through the membrane under the influence of the partial pressure difference between the two sides, effectively removing water from the solvent.
Conclusion
Damo’s pervaporation membrane technology is revolutionizing the chemical industry by providing efficient, environmentally friendly solutions for dehydration processes. With successful implementations like the acetone dehydration project in Jiangsu, Damo’s technology is proving its versatility and adaptability. The company’s collaboration with top-tier research institutions and its innovative integration of adsorption, membrane separation, and distillation technologies ensure that Damo remains at the forefront of the industry.